Using two computers, networked together, do the following to practice sharing and securing
folders using Windows XP:
1. Create a user account on Computer 1 named User1. In the My Documents folder for that
account, create a folder named Folder1.
2. On Computer 2, create a user account named User2. Try to access Folder1 on Computer 1.
What is the result? What must you do so that the folder can be accessed?
The end result is that the file isn't secured and that means any user can access this file. There are multiple ways to access this file. Both computers have the same OS and I just simply mapped both of the drives on the computers.
3. Now make the folder private so that others cannot see or access it on the network. Describe how you did that.
You can change the permissions on the folders. Right click
on the folder, select properties, open the security tab, click the
"edit" button, and remove the other users from the dialog that appears by
highlighting their username and clicking "remove". Just don't remove
yourself.
PROJECT 20-2: Download and Use AV Software
A free trial of AVG Anti-Virus software is available on the AVG site at www.avg.com. Do
the following to download, install, and run the software:
1. Download the free trial version of AVG Anti-Virus software from the www.avg.com site
and install the software.
I installed this latest free trail of AVG through Virtualbox with the OS as Windows XP.
During the installation:
After the AVG installation:
2. Perform a complete scan of the system. Were any suspicious programs found?
I scanned the computer and I did have 1 threat. It was just a corrupted ".exe file" and it was removed.
After the scan:
The end results of the scan:
3. Update the software with the latest virus signatures.
4. Set the AV software to scan the system daily.
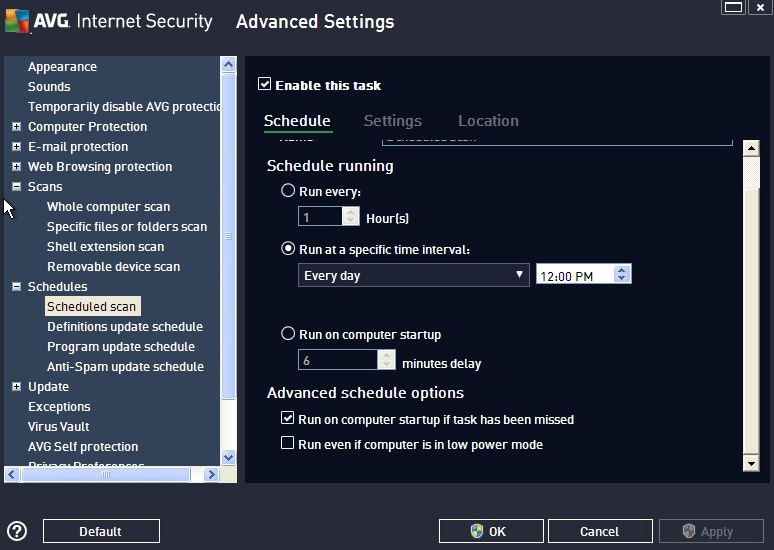
5. Set the software to scan incoming e-mail.
Boot to the Windows desktop and then use Task Manager to get a list of all the running
processes on your machine. Get a print screen of this list. Make a written list of each
process running and write a one-sentence explanation of the process. Note that you most
likely will need to use the Internet to research some of these processes.
Next, boot the system into Safe Mode and use Task Manager to list running processes.
Which processes that were loaded normally are not loaded when the system is running in
Safe Mode?
Task Manager Processes running normal:
I will make a list of five of the Processes on this list but not all 40 of them. I'm picking the Processes that look unfamiliar to me. So I can do some internet research and label them in this small list.Processes List:
- armsvc.exe - Adobe Update Service
- csrss.exe - Client Server Runtime SubSystem
- dwm.exe - The Ultimate Troubleshooter
- igfxtray.exe - Intel Graphics Tray
- smss.exe - Session Manager SubSystem
armsvc.exe - Adobe Update Service is a service that helps manually update Adobe Reader.
csrss.exe - Client Server Runtime SubSystem makes a Win32 API call, it is usually CSRSS which communicates with the operating system's Kernel to execute the API call.
dwm.exe - The Ultimate Troubleshooter has the full database in a easy interface which makes the process of fine tuning your PC, or troubleshooting your computer's problems.
igfxtray.exe - When you double click the Intel Graphics Tray on it enables you to quickly change the display resolution, save your current Display Scheme, or configure your onboard graphics card.
smss.exe - Session Manager SubSystem purpose is to start, manage, and delete user sessions.
Task Manager Processes running in Safe Mode:
You can see the difference in these pictures between Normal and Safe Mode. There are less Processes in Safe Mode, less CPU Usage, and less Physical Memory. Then in normal there is more Processes, more CPU Usage, and more Physical Memory. We definitely have a less number of Processes running while in Safe Mode.PROJECT 20-4: Learning to Use Autoruns
Autoruns by TechNet and Sysinternals (technet.microsoft.com) is similar to, but gives more
information than does MSconfig. Download Autoruns and run it on your PC. How many
registry keys does Autoruns list that contain startup items on your PC? Use Msconfig to get
a similar list. Compare the list of startup items to that generated by Msconfig. Describe any
differences between the two lists.
Autoruns:
Msconfig:
You can see a big difference between the programs here in the pictures. I prefer Autoruns because it is more detailed about everything I need to know for the computer. Msconfig I would recommend to a novice user because it's simpler. However, Msconfig doesn't give as much information specifically as Autoruns.
PROJECT 20-5: Using the Internet to Learn About Viruses
One source of information about viruses on the Web is F-Secure Corporation. Go to the
Web site www.f-secure.com, for information about viruses. Information about viruses
includes complete descriptions, symptoms, and solutions. Print a description of three viruses
from this Web site, with these characteristics:
- One virus that destroys data on a hard drive
- One harmless virus that only displays garbage on the screen
- One virus that hides in a boot sector
The site also lists information about the most recent viruses. Search the Web site at
www.f-secure.com, list three recent viruses, and describe their payloads.
I will just link the information for each of the three viruses from the "www.f-secure.com" website.
The first virus that destroys data on the hard drive is a Worm. Here is the link for more information about the Worm.
http://www.f-secure.com/v-descs/magistr.shtml
The second virus that just displays garbage on the screen is called Leningrad. Here is the link for more information about Leningrad.
http://www.f-secure.com/v-descs/crash.shtml
The third stealthy virus that hides in a boot sector is called the Boot/Brain virus. Here is the link for more information about the Boot/Brain Virus.
http://www.f-secure.com/v-descs/brain.shtml






















